Alcoholic steatosis information
Home » » Alcoholic steatosis informationYour Alcoholic steatosis images are available in this site. Alcoholic steatosis are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Alcoholic steatosis files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for alcoholic steatosis images information connected with to the alcoholic steatosis interest, you have come to the right site. Our website always provides you with hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Alcoholic Steatosis. Alcoholic steatosis, defined histologically as the deposition of fat in small or large droplets in hepatocytes, is the initial phase of ald 3. Chronic alcohol consumption induces the development of alcoholic steatosis in the liver, which is one of the most widespread liver diseases worldwide. Steatosis is accumulation of fat in the liver. Hepatic steatosis and steatohepatitis are encountered with great frequency in people who consume large amounts of ethanol (more than 6 drinks per day).
 Fat in Places You Didn�t Know Could get Fat endeavors From endeavors.unc.edu
Fat in Places You Didn�t Know Could get Fat endeavors From endeavors.unc.edu
Hepatic steatosis is reported to be associated with disturbance in the signaling cascade of interferon and downregulation of its receptors. The term “fatty degeneration” has been used when > 5% of hepatocytes show steatosis while fatty liver is the term described when > 50% of hepatocytes show steatosis. Alcoholic steatosis, defined histologically as the deposition of fat in small or large droplets in hepatocytes, is the initial phase of ald 3. Although steatosis (fatty liver disease) will develop in any individual. It is the major cause of liver disease in western countries. Treatment can help but it cannot be cured.
Chronic alcohol consumption induces the development of alcoholic steatosis in the liver, which is one of the most widespread liver diseases worldwide.
Fatty liver disease (fld), also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Alcoholic liver disease (ald) represents a spectrum of injury, ranging from simple steatosis to alcoholic hepatitis to cirrhosis. Major risk factors are obesity and diabetes type ii, it is also associated with excessive alcohol consumption. Alcoholic hepatitis (ah) is an acute hepatic. The steatosis usually resolves within 2 weeks of discontinuance of alcohol. Alcoholic steatosis (as), is the initial stage of ald, characterized by extensive fat accumulation in the liver along with mild to moderate liver injury (galambos, 1972;macsween and burt, 1986.
 Source: liveratlas.org
Source: liveratlas.org
Steatosis is defined as the accumulation of lipid droplets in the hepatocyte cytoplasm. This is swelling in the liver that can cause fever, nausea, vomiting, belly pain, and jaundice (yellowish skin and eyes). It is projected to become a leading indication for liver transplantation, superseding hepatitis c. Among others, ir is a recognized factor. The diagnosis of hepatic steatosis is based on exclusion of other aetiologies, such as alcohol use,.
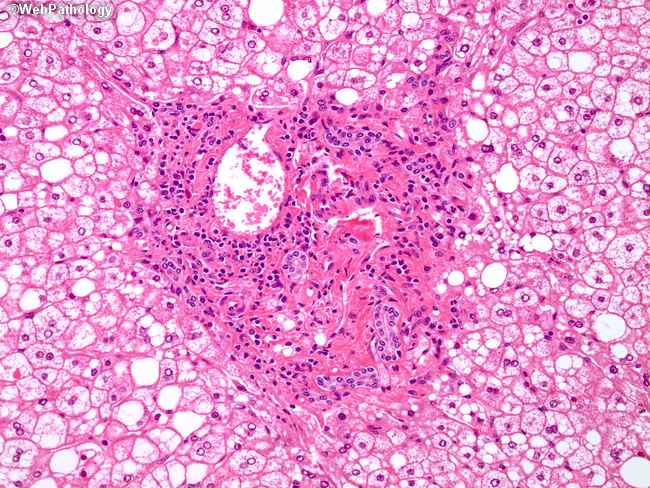 Source: webpathology.com
Source: webpathology.com
It is projected to become a leading indication for liver transplantation, superseding hepatitis c. Treatment can help but it cannot be cured. This is also known as alcoholic hepatitis. Regular alcohol use results in fatty changes in the liver which can develop into inflammation, fibrosis and ultimately cirrhosis with continued, excessive drinking. There are two types of fatty liver disease:
 Source: endeavors.unc.edu
Source: endeavors.unc.edu
This is also known as alcoholic hepatitis. Alcoholic hepatitis can range in severity from asymptomatic derangement of biochemistries to liver failure and death. The steatosis usually resolves within 2 weeks of discontinuance of alcohol. Excess fat accumulation in lipid droplets induces hepatocellular ballooning to hinder blood flow and microcirculation in sinusoidal space and consequently raises oxidative injury and endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocytes 4 , 5. They evolve from simple steatosis to cirrhosis (f4), via steatohepatitis and fibrosis (f1 to f3).
 Source: liveratlas.org
Source: liveratlas.org
There are two types of fatty liver disease: It is the major cause of liver disease in western countries. Chronic alcohol consumption induces the development of alcoholic steatosis in the liver, which is one of the most widespread liver diseases worldwide. Major risk factors are obesity and diabetes type ii, it is also associated with excessive alcohol consumption. Treatment can help but it cannot be cured.
 Source: webpathology.com
Source: webpathology.com
The term “fatty degeneration” has been used when > 5% of hepatocytes show steatosis while fatty liver is the term described when > 50% of hepatocytes show steatosis. It is projected to become a leading indication for liver transplantation, superseding hepatitis c. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Complications may include cirrhosis, liver cancer, and esophageal varices. Alcoholic steatosis (as), is the initial stage of ald, characterized by extensive fat accumulation in the liver along with mild to moderate liver injury (galambos, 1972;macsween and burt, 1986.
 Source: humpath.com
Source: humpath.com
The term “fatty degeneration” has been used when > 5% of hepatocytes show steatosis while fatty liver is the term described when > 50% of hepatocytes show steatosis. Major risk factors are obesity and diabetes type ii, it is also associated with excessive alcohol consumption. Ethanol causes steatosis by altering several steps in the hepatic processing of fatty acids, including their uptake from plasma, their use as fuel s. The fat that accumulates is mainly triglyceride and can be attributed to the effects of alcohol metabolism on hepatic fatty acid synthesis. Alcoholic steatosis, defined histologically as the deposition of fat in small or large droplets in hepatocytes, is the initial phase of ald 3.
 Source: humpath.com
Source: humpath.com
Alcoholic steatosis (as), is the initial stage of ald, characterized by extensive fat accumulation in the liver along with mild to moderate liver injury (galambos, 1972;macsween and burt, 1986. Improper use of alcohol affects 20 to 25% of the population; Among others, ir is a recognized factor. The steatosis usually resolves within 2 weeks of discontinuance of alcohol. This is also known as alcoholic hepatitis.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title alcoholic steatosis by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
Category
Related By Category
- Cheap dog grooming information
- Best car restoration information
- All car restorations information
- Buy dog clothes online information
- Causes for childhood obesity information
- First aid courses london information
- Dream interpretation worms information
- First aid course toronto information
- Dash diet summary information
- Flatulence foods information