Fatty change liver information
Home » » Fatty change liver informationYour Fatty change liver images are ready in this website. Fatty change liver are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Fatty change liver files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for fatty change liver pictures information related to the fatty change liver topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website always provides you with hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
Fatty Change Liver. Increase of free fatty acids (starvation, diabetes and chronic ethylism / alcoholism), reduction of free fatty acids oxidation (hypoxia, toxins, chronic ethylism/alcoholism), increase of esterification of free. These changes, especially when they are large and single, pose an important diagnostic problem as their clinical and radiological picture may imitate malignancy. It is normal for the liver to contain some fat, but if fat accounts for more than 10 per cent of the liver’s weight, then you have fatty liver and you may develop more serious complications. Synonyms for fatty change liver in free thesaurus.
 Fatty Change (Fatty Metamorphosis) The Digitized Atlas From niehs.nih.gov
Fatty Change (Fatty Metamorphosis) The Digitized Atlas From niehs.nih.gov
Often there are no or few symptoms. In some cases, though, it can lead to liver damage. A �billable code� is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. What are synonyms for fatty change liver? If there is too much, you have fatty liver. The pathology narrative should also include the pathologist’s opinions regarding the contents of the cytoplasmic vacuoles.
Deposition of fat in the hepatocyte cytoplasm often displaces the hepatocyte nucleus to the periphery of the cell.
K76.0 is a billable icd code used to specify a diagnosis of fatty (change of) liver, not elsewhere classified. Fatty change or steatosis represents the intracytoplasmic accumulation of triglyceride (neutral fats) of parenchimal organs, such as: It�s usually seen in people who are overweight or obese. The large, sharply delineated, clear vacuoles represent macrovesicular fat that has been dissolved during tissue processing. Most people have no symptoms, and it doesn’t cause serious problems for them. These changes, especially when they are large and single, pose an important diagnostic problem as their clinical and radiological picture may imitate malignancy.
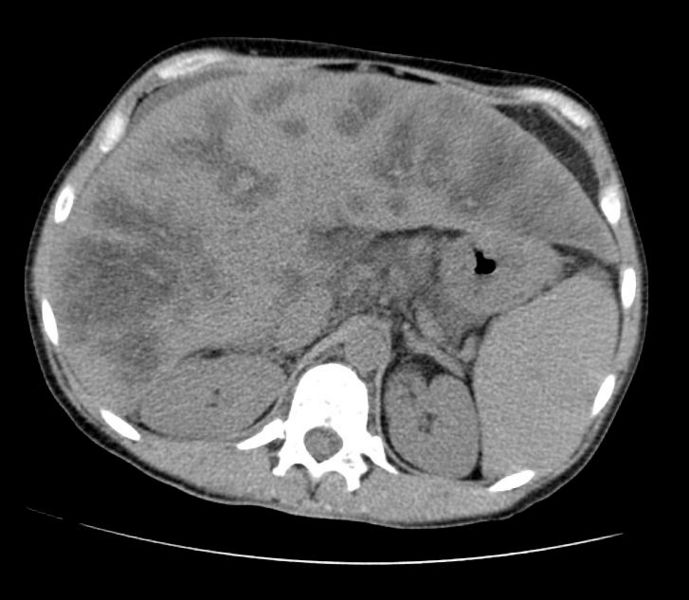 Source: wikidoc.org
Source: wikidoc.org
Fatty liver, or hepatic steatosis, is a broad term that describes the buildup of fats in the liver. In contrast, figure 5 and figure 6 are representative of microvesicular fatty change, with a more prominent response in periportal and midlobular areas. These changes, especially when they are large and single, pose an important diagnostic problem as their clinical and radiological picture may imitate malignancy. Fatty liver disease is a common condition caused by the storage of extra fat in the liver. Patients are often asymptomatic but the condition can progress to hepatitis or cirrhosis if the underlying cause is not removed.
 Source: niehs.nih.gov
Source: niehs.nih.gov
A normal healthy liver compared to one with fatty liver disease where the fat is stored in the liver cells. Deposition of fat in the hepatocyte cytoplasm often displaces the hepatocyte nucleus to the periphery of the cell. Too much fat in the liver can cause liver inflammation and liver damage. Complications may include cirrhosis, liver cancer, and esophageal varices. Synonyms for fatty change liver in free thesaurus.
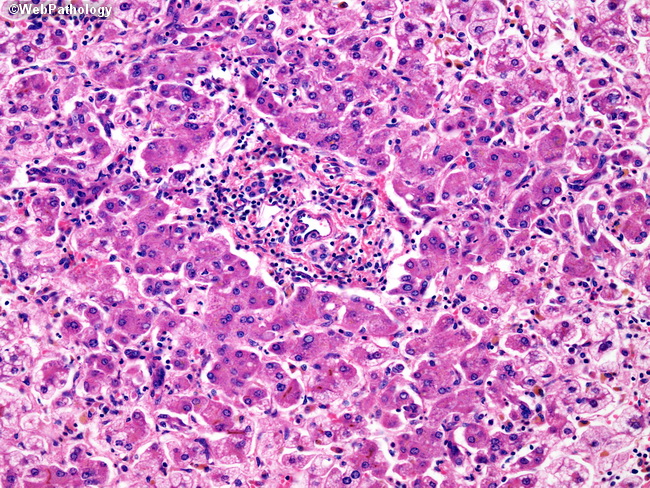 Source: webpathology.com
Source: webpathology.com
Increase of free fatty acids (starvation, diabetes and chronic ethylism / alcoholism), reduction of free fatty acids oxidation (hypoxia, toxins, chronic ethylism/alcoholism), increase of esterification of free. Fatty liver is becoming more common throughout the western world because we are eating too many added sugars and added fats. Increase of free fatty acids (starvation, diabetes and chronic ethylism / alcoholism), reduction of free fatty acids oxidation (hypoxia, toxins, chronic ethylism/alcoholism), increase of esterification of free. Focal fatty change (ffc) may occur in the form of a single or numerous nodules of different size, located in the liver with otherwise normal structure. A normal healthy liver compared to one with fatty liver disease where the fat is stored in the liver cells.
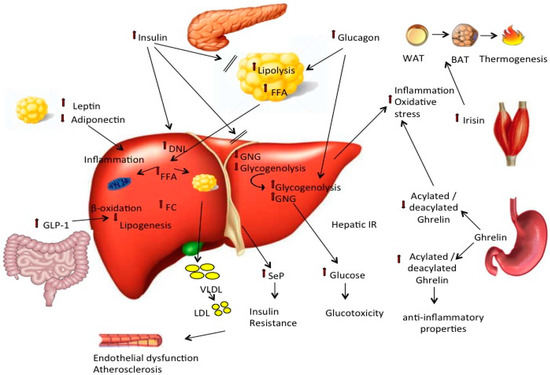 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Too much fat in the liver can cause liver inflammation and liver damage. Fatty liver, or hepatic steatosis, is a broad term that describes the buildup of fats in the liver. Focal fatty change first described in 1980 (gastroenterology 1980;78:247) clinical features rare, often incidental finding at autopsy or misinterpreted on imaging as. In contrast, figure 5 and figure 6 are representative of microvesicular fatty change, with a more prominent response in periportal and midlobular areas. A healthy liver should contain little or no fat.
 Source: niehs.nih.gov
Source: niehs.nih.gov
A healthy liver should contain little or no fat. Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Too much fat in the liver can cause liver inflammation and liver damage. Fat is in large droplets and the liver is enlarged but of normal consistency; The large, sharply delineated, clear vacuoles represent macrovesicular fat that has been dissolved during tissue processing.
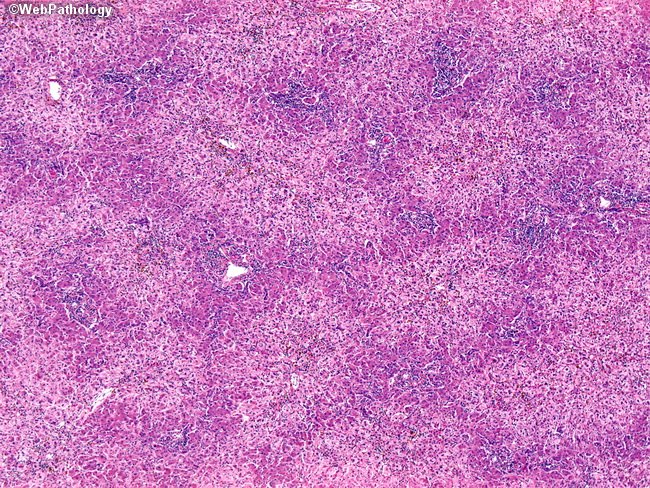 Source: webpathology.com
Source: webpathology.com
Fatty liver one affected with fatty infiltration, usually from alcohol abuse, jejunoileal bypass surgery, or occasionally diabetes mellitus; Depending upon its etiology , it is divided into two types : Patients are often asymptomatic but the condition can progress to hepatitis or cirrhosis if the underlying cause is not removed. Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Fatty change or steatosis represents the intracytoplasmic accumulation of triglyceride (neutral fats) of parenchimal organs, such as:
 Source: radiologyinthai.blogspot.com
Source: radiologyinthai.blogspot.com
Increase of free fatty acids (starvation, diabetes and chronic ethylism / alcoholism), reduction of free fatty acids oxidation (hypoxia, toxins, chronic ethylism/alcoholism), increase of esterification of free. These changes, especially when they are large and single, pose an important diagnostic problem as their clinical and radiological picture may imitate malignancy. Fatty liver is becoming more common throughout the western world because we are eating too many added sugars and added fats. Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Most people have no symptoms, and it doesn’t cause serious problems for them.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title fatty change liver by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
Category
Related By Category
- Cheap dog grooming information
- Best car restoration information
- All car restorations information
- Buy dog clothes online information
- Causes for childhood obesity information
- First aid courses london information
- Dream interpretation worms information
- First aid course toronto information
- Dash diet summary information
- Flatulence foods information